1 清华大学精密仪器系,北京 100084
2 光子测控技术教育部重点实验室,北京 100084
随着人工智能技术的飞速发展与广泛应用,人们对计算资源的需求日益增长,面对电子摩尔定律所遇到的原理性瓶颈,光子以高传输速度、高并行度等优势成为研究人员心目中的下一代计算机载体之一。近年来的研究工作显示,激光谐振腔内许多有趣的物理现象和复杂的动态演化过程能够被用于各种各样的数据处理与计算任务,极大地拓展了激光器的应用范围。在这篇综述中,笔者对基于激光谐振腔的智能光子计算的研究进展进行了集中的介绍与梳理,主要内容涵盖利用激光腔内的混沌过程辅助光电强化学习、利用光反馈激光器的非线性信号变换构建光电储备池网络,以及利用激光网络向稳定振荡状态的自发演化求解组合优化问题。在介绍相关最新进展之余,笔者分析讨论了智能激光计算系统面临的挑战,并对其未来的发展趋势进行了展望。
光计算 激光器 人工智能 光电强化学习 光电储备池计算 光学伊辛机 中国激光
2023, 50(11): 1101002
浙江科技学院理学院应用物理系, 杭州 310023
酒精中低浓度甲醇和乙醇的精准检测是十分重要的。低频拉曼散射是研究液相分子间相互作用最有效的方法之一。本文采用新型超低频拉曼光谱, 对不同浓度的乙醇以及乙醇-甲醇混合液进行研究。实验发现, 不同浓度下乙醇溶液在78 cm-1和170 cm-1存在两个特征峰, 不同浓度下乙醇-甲醇混合液在85 cm-1和178 cm-1存在两个特征峰。其中, 78 cm-1特征峰是由于OH-O伸缩振动引起的, 178 cm-1特征峰是由于OH-O面内弯曲振动引起的, 85 cm-1和170 cm-1两个峰是由C-OH的伸缩振动引起的。同时, 我们发现了以上超低频特征峰频率与乙醇以及乙醇-甲醇混合液浓度的依赖关系, 能够为较低浓度的乙醇和甲醇溶液精确指认提供可借鉴的实验思路和依据。
超低频拉曼光谱 乙醇 甲醇 Ultra-low frequency Raman spectroscopy Ethanol Methanol
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China
2 State Key Laboratory of Electrical Insulation and Power Equipment, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an 710049, China
3 Global Energy Interconnection Development and Cooperation Organization, Beijing 100031, China
4 Systems Engineering Research Institute, Beijing 100094, China
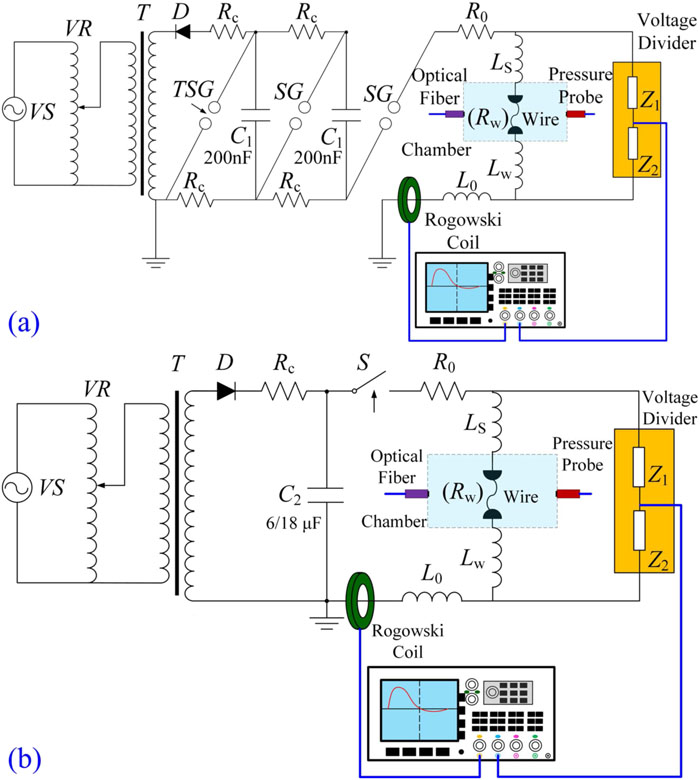
Underwater shock waves generated by pulsed electrical discharges are an effective, economical, and environmentally friendly means of stimulating reservoirs, and this technology has received much attention and intensive research in the past few years. This paper reviews the main results of recent work on underwater electrical wire explosion (UEWE) for reservoir stimulation. A platform is developed for microsecond single-wire explosions in water, and diagnostics based on a voltage probe, current coil, pressure probe, photodiode, and spectrometer are used to characterize the UEWE process and accompanying shock waves. First, the UEWE characteristics under different discharge types are studied and general principles are clarified. Second, the shock-wave generation mechanism is investigated experimentally by interrupting the electrical energy injection into the wire at different stages of the wire-explosion process. It is found that the vaporization process is vital for the formation of shock waves, whereas the energy deposited after voltage collapse has only a limited effect. Furthermore, the relationships between the electrical-circuit and shock-wave parameters are investigated, and an empirical approach is developed for estimating the shock-wave parameters. Third, how the wire material and water state affect the wire-explosion process is studied. To adjust the shock-wave parameters, a promising method concerning energetic material load is proposed and tested. Finally, the fracturing effect of the pulsed-discharge shock waves is discussed, as briefly are some of the difficulties associated with UEWE-based reservoir stimulation.
Matter and Radiation at Extremes
2020, 5(4): 047201

Dong Pan 1,2†Zaisheng Lin 2,3,4,5†Jiawei Wu 1,2Haoran Zhang 1,2[ ... ]Gui Lu Long 1,2,3,4,5,7,*
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Low-dimensional Quantum Physics and Department of Physics, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
2 Frontier Science Center for Quantum Information, Beijing 100084, China
3 School of Information Science and Technology, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
4 Beijing National Research Center for Information Science and Technology, Beijing 100084, China
5 Beijing Academy of Quantum Information Sciences, Beijing 100193, China
6 e-mail: yinlg@tsinghua.edu.cn
7 e-mail: gllong@tsinghua.edu.cn
We report an experimental implementation of free-space quantum secure direct communication based on single photons. The quantum communication scheme uses phase encoding, and the asymmetric Mach–Zehnder interferometer is optimized so as to automatically compensate phase drift of the photons during their transitions over the free-space medium. At a 16 MHz pulse repetition frequency, an information transmission rate of 500 bps over a 10 m free space with a mean quantum bit error rate of is achieved. The security is analyzed under the scenario that Eve performs the collective attack for single-photon state and the photon number splitting attack for multi-photon state in the depolarizing channel. Our results show that quantum secure direct communication is feasible in free space.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(9): 09001522
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Institute for Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China
2 School of Electronic Information Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
We propose improved multilevel filters (IMLFs) involving the absolute value operation into the algorithmic framework of traditional multilevel filters (MLFs) to improve the robustness of infrared small target enhancement techniques under a complex infrared cluttered background. Compared with the widely used small target enhancement methods which only deal with bright targets, the proposed technique can enhance the infrared small target, whether it is bright or dark. Experimental results verify that the proposed technique is efficient and practical.
红外小目标 目标增强 多级滤波 杂波背景 100.3008 Image recognition, algorithms and filters 100.2000 Digital image processing 100.2960 Image analysis 100.0100 Image processing Chinese Optics Letters
2011, 9(5): 051001





